
Scheuermann’s Disease Radsource
Scheuermann's disease (SD) is a progressive disease associated with back pain or low back pain in adolescents. It is the most common cause of structural thoracic or thoracolumbar hyperkyphosis, and could be seen in typical or atypical patterns. Diagnosis of SD is made by radiological methods along with clinical findings.

Morbus Scheuermann Gesundheitsportal Medavit De My XXX Hot Girl
Scheuermann disease is an osteochondrosis that causes localized changes in vertebral bodies, leading to backache and kyphosis. Diagnosis is with spinal x-rays. Treatment usually involves only reduction of weight bearing and strenuous activity. Scheuermann disease manifests in adolescence and is slightly more common among boys.
Scoliosis and Kyphosis, what's the difference? Scoliosis Clinic UK Treating Scoliosis
Notably, both classic SD and atypical SD are associated with back pain. 14, 16, 17, 19 - 22 Although Scheuermann kyphosis is uncommon, SD radiological signs have been observed in 18% to 40% of the general population, 23 suggesting that SD, or more precisely, "SD-like" spine, may be a variant of normal spine morphology rather than a.

Figure 10 from Radiological imaging findings of scheuermann disease Semantic Scholar
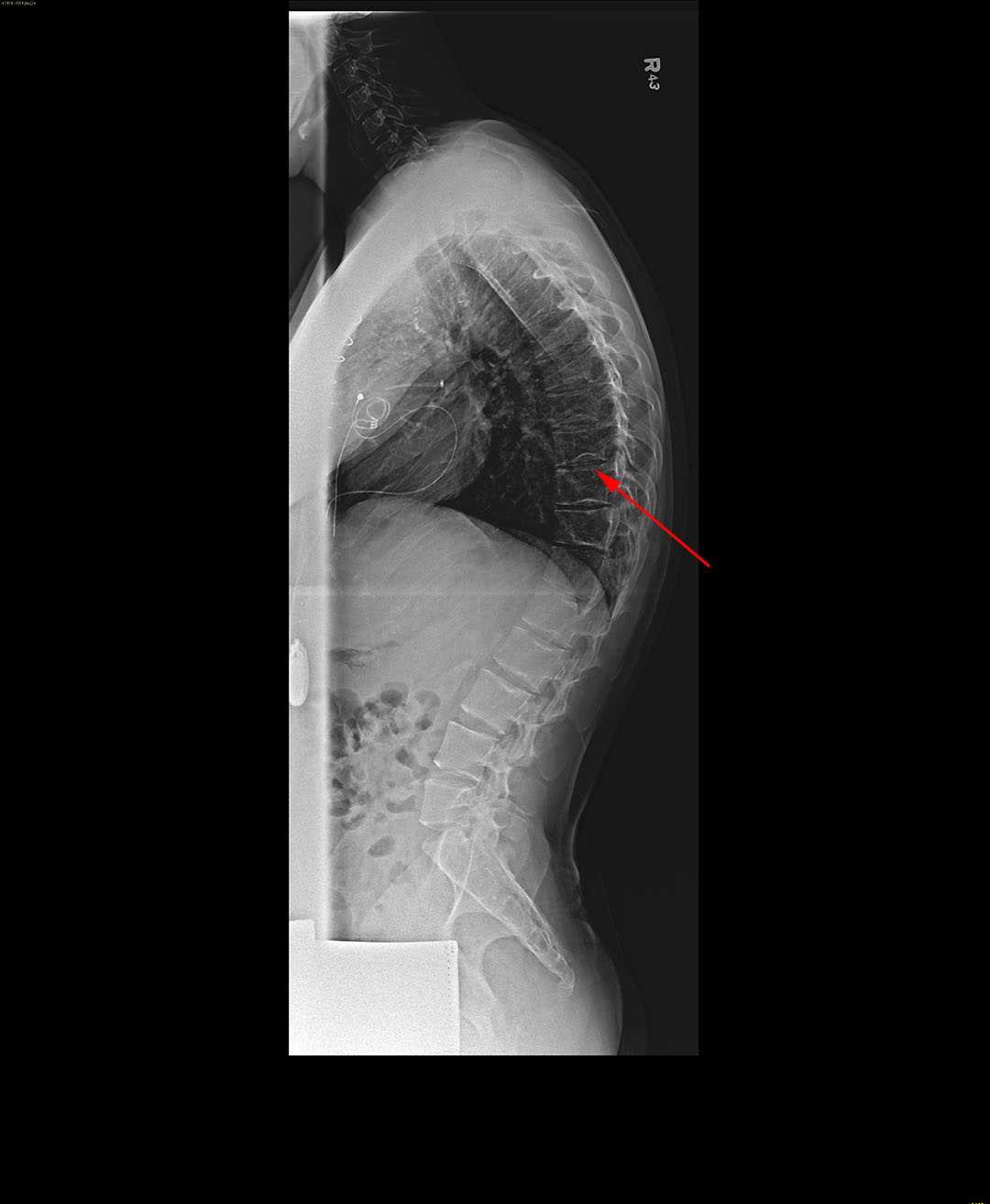
STIR. Coronal. STIR. Axial. T2. Decreased lower thoracic and lumbar vertebral height, associated with marked irregularity of end-plates and formation of multiple prominent Schmorl's nodes. The AP diameter of the spinal canal gradually decreases as the level lowers.

Scheuermann’s Disease Radsource
Scheuermann's Kyphosis (SK), first described by Horgel Welfer Scheuermann in 1920, is a rigid spinal kyphosis usually involving the thoracic or thoracolumbar area ( 1 ). Albeit several theories, its etiology is still unknown ( 2 ). SK is usually separated into two groups: typical and atypical SK. Typical SK is the more common type and has a mid.

Scheuermann's disease Radiology Case
Therefore, in the present study, we aimed to evaluate the radiological pathomorphological features of the spine and the association between the thoracic kyphosis angle and the clinical presentation by assessing pain and self-perceived body image in patients with Scheuermann's disease. We proposed two hypotheses.

Scheuermann’s Disease Neupsy Key
Lumbar Scheuermann disease is a type of variant Scheuermann disease where there is no abnormal kyphosis. This has been reported in the lumbar spine and thoracolumbar junction of patients of all ages, and back pain may be present. On imaging, affected individuals can have vertebral endplate changes, disc space narrowing, and anterior Schmorl.

Scheuermann disease Radiology Case
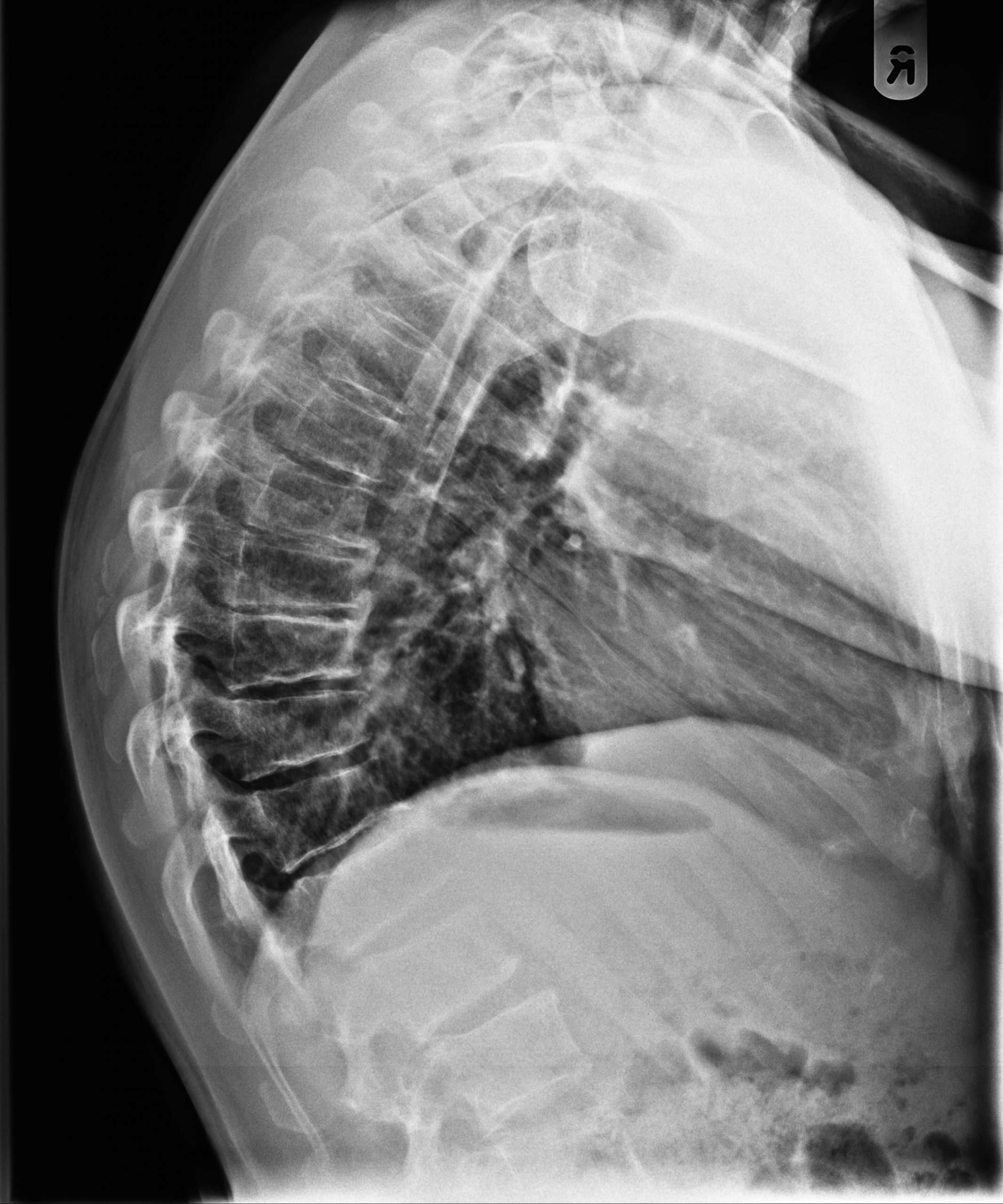
Scheuermann disease, (juvenile kyphosis), is a growth disturbance with curving deformity of the thoracic or thoracolumbar spine in adolescents that causes an increase bowing or rounding of the back in the sagittal plane. It is defined by anterior vertebral wedging of at least 5° in 3 or more adjacent vertebral bodies.

Scheuermann disease presenting as compressive myelopathy Neurology
Gender: Female. x-ray. Vertebral wedging, subchondral osseous irregularity in the endplates, Schmorl's nodes and an asymptomatic thin cleft in the neural arch of the fifth lumbar vertebra. There's also hypoplasia of the left iliac bone and mild hypoplasia of the ipsilateral proximal femur.

Scheuermann disease Radiology Case Radiology, Disease, Thoracic vertebrae
Scheuermann kyphosis, also known as Scheuermann disease, juvenile kyphosis, or juvenile discogenic disease, is a condition of hyperkyphosis that involves the vertebral bodies and discs of the spine identified by anterior wedging of greater than or equal to 5 degrees in 3 or more adjacent vertebral bodies. The thoracic spine is most commonly involved, although involvement can include the.

Scheuermann disease Image
Scheuermann Disease / therapy*. Thoracic Vertebrae / diagnostic imaging. Recent studies have revealed a major genetic contribution (a dominant autosomal inheritance pattern with high penetrance and variable expressivity) to the etiology of Scheuermann kyphosis with a smaller environmental component (most probably mechanical factors).

Image
Aim: To find accompanying anomalies of typical and atypical Scheuermann's disease (SD) is reported in the present study. Methods: Study included 20 patients (16 men and 4 women) who had radiological imaging radiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography, if available, due to back pain, curved back and low back pain in November 2011-February 2016 period.

Scheuermann's Kyphosis Spine Orthobullets
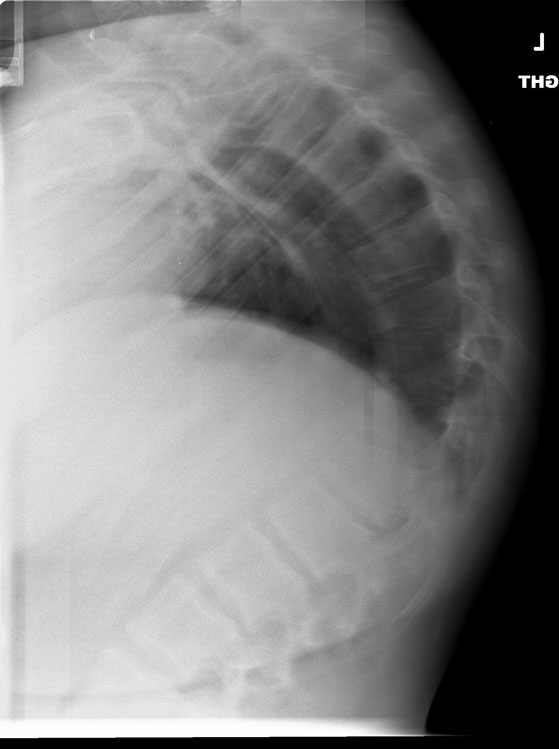
Case Discussion. A rare example of Scheuermann disease "caught in the act", that may eventually result in kyphosis. Also note the persisting neurocentral synchondroses typical for that age.
Scheuermann's Disease X Rays Case Studies CTisus CT Scanning
Scheuermann's kyphosis (SK) is a rigid spinal kyphosis affecting the mid-thoracic or thoracolumbar spine, which was first described by Holger Werfel Scheuermann in 1920. 1, 2 The condition is associated with anterior wedging of the vertebrae, end plate irregularities, and Schmorl's nodes. 3 In 1964, Sorensen 4 was the first to define SK radiographically by the presence of at least three.

Scheuermann’s Disease Radsource
A-Z of Musculoskeletal and Trauma Radiology - June 2008. To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account.
Hyperkyphosis Scheuermanns Disease
Introduction. Scheuermann's disease (SD), also known as Scheuermann's juvenile kyphosis or juvenile osteochondrosis of the spine, was first described by Holger Scheuermann in 1920. SD develops prior to the onset of puberty, typically presenting during the adolescent growth spurt as a rigid, sometimes painful thoracic kyphosis. 1.